The Boss decided interest rate will stay a.k.a. Money Is Almost Free.
Yeah, right … Free.
Dream on. The bank will still charge you a few percents even the rate falls to sub zero region ie. below 0%.
As a matter of fact, based on today’s circumstances, what else can the government do?
If they raise the interest rate, the whole economy will crumble down. If they don’t … don’t be surprise you wake up one day just to find a loaf of bread costs $1 million … This phenomenon is called hyper-inflation. And inflation is one of the necessary evil twin of low interest rate.
 Image Source
Image Source
Most people love low interest rate, but some don’t …
Why ?
Because those don’t fancy low interest know there is no free lunch. It comes with a price. In our case, a hefty price to pay back for a long, long time to come …
One of the answers is right here: –
What is the relationship between inflation and interest rates?
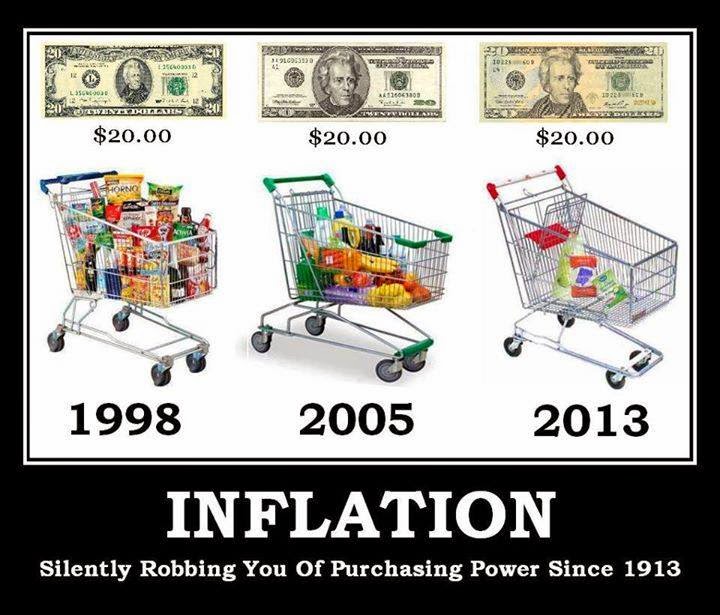 Image Source
Image Source
By Jean Folger
Answer:
Inflation and interest rates are linked, and frequently referenced in macroeconomics. Inflation refers to the rate at which prices for goods and services rises. In the United States, interest rates are determined by the Federal Reserve (sometimes called “the Fed”). In general, as interest rates are lowered, more people are able to borrow more money. The result is that consumers have more money to spend, causing the economy to grow and inflation to increase. The opposite holds true for rising interest rates. As interest rates are increased, consumers tend to save as returns are higher. With less disposal income to spend as a result of the increase in savings, the economy slows and inflation decreases.
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meets eight times each year to review economic and financial conditions and decide on monetary policy. Monetary policy refers to the actions taken that affect the availability and cost of money and credit. At these meetings, short-term interest rate targets are determined. Using economic indicators such as the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and the Producer Price Indexes (PPI), the Fed will establish interest rate targets intended to keep the economy in balance. By moving interest rate targets up or down, the Fed attempts to achieve maximum employment, stable prices and stable economic growth. The Fed will raise interest rates to reduce inflation. Conversely, the Fed will ease (or decrease) rates to spur economic growth.
Investors and traders keep a close eye on the FOMC rate decisions. After each of the eight FOMC meetings, an announcement is made regarding the Fed’s decision to increase, decrease or maintain key interest rates. Certain markets may move in advance of the anticipated interest rate changes and in response to the actual announcements. For example, the U.S. dollar typically rallies in response to an interest rate increase.
Source: Investopedia
More related stories …
Post-Brexit, low interest rates loom as greatest danger to pension …
What will an interest rate cut by the Bank of England mean for you?
However, there are opportunities in every crisis …
How To Make Money When Interest Rates Are Low